Graceli theory carousel system. Abstract algebra and theory of graceli systems.
Imagine a dynamic cyclic system and categories of groups and ring systems [real numbers, and dimensions] that is represented by a carousel with motion x, while children with egg [that represent functions placed at specific points of the carousel.
What we have numbers of turns of the carousel turns numbers + + number of children of children, in which each function w expecifico point we placed at that point.
Or even an octagonal buds schemes system of a ball in rotation and precession [spin oscillations], more oscillatory flow, wherein in each point of each section to have a w medial function graceli + varying depending graceli [kind of progression , logarithm, root, or other] in relation to a central point, or an observer [references and relative].
That this system can be associative, commutative, or others.
That is, the system in addition to being cyclic be commutative, associative, or other in which the function can come filled operators and symbols graceli []., Or even that the functions may have weight [multiplicative factor, divisible from addition, subtraction, or others].
Theory spiral system.
That is, as the spiral enlarges a progressive relationship between the cyclical functions expiral progressively increases according to increase in size.
Teoria Graceli do sistema carrocel. Álgebra abstrata e
teoria dos sistemas Graceli.
Imagine um sistema cíclico dinâmico e de categorias de
sistemas de grupos e anéis [de números reais, e dimensões] em que é representado por um carrocel com
movimento x, enquanto crianças com ovos [que representam funções colocam em
pontos específicos do carrocel.
O que temos números de voltas do carrocel + números de
voltas das crianças + quantidade de crianças, em que em cada ponto expecifico
teremos w funções colocadas naquele ponto.
Ou mesmo um sistema de esquemas de gomos octogonal de
uma bola em rotação e precessão [oscilações de rotação], mais fluxos
oscilatórios, em que em cada ponto de cada gomo se tem uma função w medial
Graceli + função de variação graceli [tipo de progressão, logaritmo, raiz, ou
outras] em relação a um ponto central, ou a um observador [referenciais e
relativos].
Em que este sistema pode ser associativo, comutativo,
ou outros.
Ou seja, o sistema alem de ser cíclico pode ser
comutativo, associativo, ou outros, em que a função pode vir recheada de
operadores e símbolos de graceli [
]., ou mesmo que as funções podem ter peso [fator multiplicativo,
divisivel, de adição, subtração, ou outros].
Teoria do sistema espiral.
Ou seja, conforme o espiral aumenta de tamanho num
cíclico progressivo a relação entre funções aumenta progressivamente conforme a
expiral aumenta de tamanho.
.
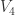 .
.  ou
ou 
 [n] + r + [â * p]...........
[n] + r + [â * p]...........
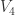 .
.  ou
ou 
 [n] + r + [â * p/pP]...........
[n] + r + [â * p/pP]...........
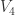 .
.  ou
ou 
 [n] + r + [â * p/pP].{toG].[n-dim].[fmG]}.
[n] + r + [â * p/pP].{toG].[n-dim].[fmG]}.
Temos um sistema em rotação e espiral crescente geométrico n-dimensional e com a função medial Graceli.
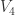 .
.  ou
ou 
 [n] + r + [â * p/pP].{toG]........
[n] + r + [â * p/pP].{toG]........

 " . c . d [n]
" . c . d [n]  , abac,[n]
, abac,[n] 
 [c. [d] [n],
[c. [d] [n], 
